Water quality affects human health, agriculture, industrial production, and environmental sustainability. Whether you are testing drinking water, managing irrigation systems, operating industrial boilers, or monitoring aquaculture tanks, you will often encounter three common parameters: PPM, TDS, and EC.
However, many users struggle to understand how these measurements relate to each other. Is TDS the same as ppm? Why does EC show different values? How do these numbers influence water safety?
Misinterpreting these values can lead to:
- Improper water treatment
- Equipment corrosion
- Crop damage
- Health risks
This is why understanding PPM vs TDS vs EC in water testing is essential for both professionals and everyday users.
This comprehensive guide explains the science, calculations, practical examples, case studies, and tools needed to interpret these parameters accurately.
What Is PPM in Water Testing?
Understanding Parts Per Million
Parts per million (ppm) represents the amount of a dissolved substance in one million parts of water.
In most water applications:
1 ppm ≈ 1 mg/L
Because 1 liter of water weighs approximately 1 kilogram, ppm and mg/L are usually interchangeable.
Why PPM Is Widely Used
PPM is popular in water testing because it:
✔ Is easy to understand
✔ Reflects concentration measurement
✔ Is accepted by regulators
✔ Works for drinking and industrial water
PPM is fundamental to ppm calculation, regulatory compliance, and water treatment operations.
What Is TDS (Total Dissolved Solids)?
Definition of TDS
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) refers to the total concentration of dissolved inorganic and organic substances in water.
It includes:
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Chlorides
- Sulfates
- Carbonates
TDS is usually reported in:
mg/L or ppm
How TDS Is Measured
TDS can be measured by:
- Gravimetric method (laboratory drying)
- Electronic meters (via EC conversion)
Most portable TDS meters estimate TDS from EC values.
What Is EC (Electrical Conductivity)?
Definition of EC
Electrical Conductivity (EC) measures water’s ability to conduct electrical current, which depends on the concentration of dissolved ions.
Units:
- µS/cm (microsiemens per centimeter)
- mS/cm (millisiemens per centimeter)
Why EC Matters
EC is important because:
✔ It responds instantly to changes
✔ Indicates ionic strength
✔ Helps monitor salinity
✔ Supports irrigation and industrial control
Unlike ppm and TDS, EC does not directly measure mass—it measures electrical behavior.

Relationship Between PPM, TDS, and EC
Fundamental Connection
Most water testers use this relationship:
TDS (ppm) = EC (µS/cm) × Conversion Factor
Where:
Conversion factor = 0.5 to 0.7 (depends on water type)
Typical Conversion Factors
| Water Type | Factor |
|---|---|
| Drinking water | 0.5 |
| Natural water | 0.55 |
| Agricultural water | 0.65 |
| Industrial water | 0.7 |
Example
EC = 800 µS/cm
Factor = 0.5
TDS = 800 × 0.5 = 400 ppm
PPM Formula and Calculation Methods
Standard PPM Formula
PPM = (Mass of Solute / Volume of Water) × 1,000,000
For water:
PPM ≈ mg/L
Practical Formula from EC
PPM ≈ EC × Factor
This method is widely used in portable meters.
Calculation Walkthrough: Converting EC to PPM
Scenario
A farmer tests irrigation water.
Measured:
EC = 1,200 µS/cm
Factor = 0.65
Step 1: Apply Formula
PPM = 1,200 × 0.65 = 780 ppm
Step 2: Interpretation
780 ppm = Moderate salinity
May affect sensitive crops
This is a practical ppm example used in agriculture.
Comparison Table: PPM vs TDS vs EC in Water Testing
| Feature | PPM | TDS | EC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement Type | Mass-based | Total mass | Electrical |
| Unit | ppm, mg/L | ppm, mg/L | µS/cm |
| Direct Measurement | Lab | Lab/Meter | Sensor |
| Accuracy | High | Medium–High | High |
| Influenced by Ion Type | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Regulatory Use | High | Medium | Low |
This table highlights why all three parameters are needed.
Applications of PPM, TDS, and EC in Industry
1. Drinking Water Systems
- PPM: Contaminant limits
- TDS: Taste and palatability
- EC: Distribution monitoring
Example:
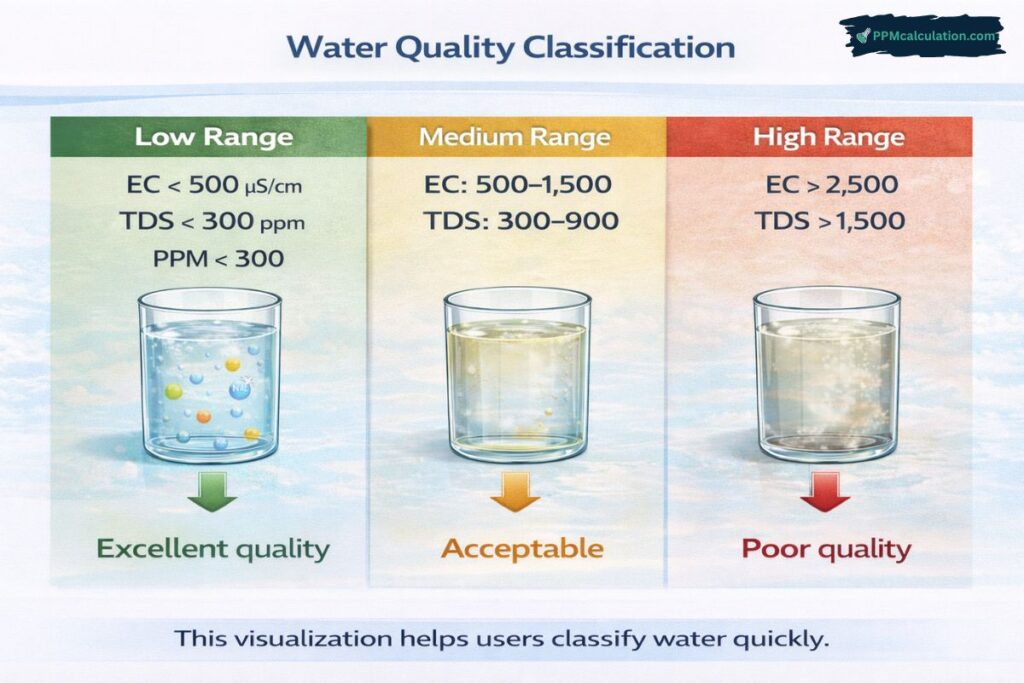
TDS < 500 ppm recommended
2. Agriculture and Irrigation
| Parameter | Role |
|---|---|
| PPM | Nutrient control |
| TDS | Salinity |
| EC | Root zone monitoring |
High EC damages crops.
3. Industrial Boilers and Cooling Towers
- PPM: Chemical dosing
- TDS: Scaling control
- EC: Blowdown control
Improper control increases maintenance costs.
4. Aquaculture and Aquariums
Stable ppm and EC levels ensure fish health.
Industry Case Study 1: Boiler Scaling Failure
Background
A factory ignored rising TDS.
Readings:
- EC: 2.5 mS/cm
- TDS: 1,750 ppm
Result
- Severe scaling
- Heat transfer loss
- ₹45 lakh repair cost
Lesson
Integrated monitoring prevents failures.
Industry Case Study 2: Crop Loss Due to Salinity
Scenario
Greenhouse irrigation water:
EC = 3.0 mS/cm
PPM ≈ 1,950
Sensitive crops failed.
Solution
RO treatment reduced TDS to 300 ppm.
Yield recovered.
PPM to mg/L Conversion in Water Testing
General Rule
1 ppm = 1 mg/L
For freshwater systems.
Example
Nitrate = 8 mg/L
= 8 ppm
This simplifies regulatory reporting.
Tools & Calculators for PPM, TDS, and EC
Manual conversion is error-prone. Digital tools improve accuracy.
Trusted Platform: ppmcalculation.com
ppmcalculation.com provides professional-grade tools for water testing:
Advantages
- Scientifically validated formulas
- Instant results
- Mobile compatibility
- No registration
- Error-free outputs
These tools simplify ppm calculation for all users.
Common Mistakes in Interpreting PPM, TDS, and EC
1. Assuming Fixed Conversion Factors
Different waters require different factors.
2. Ignoring Temperature Effects
EC changes with temperature.
3. Confusing TDS and PPM
TDS includes total load, ppm may target specific ions.
4. Over-Reliance on Cheap Meters
Low-quality sensors distort readings.
5. Skipping Calibration
Uncalibrated meters produce misleading data.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is TDS the same as ppm?
TDS is usually expressed in ppm, but it represents total dissolved material.
2. Which is more accurate: EC or TDS?
EC is more precise for real-time monitoring. TDS depends on conversion.
3. What is ideal TDS for drinking water?
Between 50 and 500 ppm is generally acceptable.
4. Can EC detect toxic metals?
No. EC shows total ions, not specific contaminants.
5. Why do two meters give different ppm values?
Different conversion factors and calibration methods.
6. Is ppm enough for full water quality analysis?
No. It must be combined with chemical testing.
PPM vs TDS vs EC in Water Testing
Understanding PPM vs TDS vs EC in water testing allows users to interpret water quality accurately and make informed decisions.
Key Takeaways
✔ PPM measures concentration
✔ TDS measures total dissolved load
✔ EC measures ionic conductivity
✔ All three are interconnected
✔ Proper conversion prevents errors
Together, these parameters provide a complete picture of water quality.
Related PPM Calculators
Explore more water quality and chemistry tools:



