PPM in water quality is used to measure how much of a substance is dissolved in water. It stands for parts per million, which means one part of a chemical, mineral or contaminant mixed into one million parts of water. Because many water impurities are found in very small amounts, PPM measurement helps determine whether water is safe, clean, and healthy to drink.
Water quality experts use PPM concentration to monitor drinking water, groundwater, wastewater, aquarium water and pool water. Whether the focus is minerals, chemicals, or pollutants, PPM provides a simple number that shows how clean or contaminated the water really is.
What Does 1 PPM Mean in Water
One PPM means there is one milligram of a dissolved substance in one litre of water. This works because one litre of pure water weighs 1,000,000 mg, making 1 mg/L equal to 1 PPM. Even though the amount is tiny, some substances can affect taste, smell, health, or safety at only a few PPM.
Example
If water contains 2 mg of chlorine per litre, the chlorine level is 2 PPM. That means out of one million parts of water, only two parts are chlorine.
Why PPM Is Important for Water Safety
Water quality PPM levels determine whether the water is suitable for human use. Too many dissolved solids or chemicals can cause water to become unsafe. High PPM can lead to metal contamination, health risks, bad taste, and pipe corrosion. Low PPM can also be a problem when disinfectant levels drop too low, allowing bacteria to grow.
Therefore, PPM water analysis ensures water remains safe for drinking, cooking, cleaning and bathing.
Common Substances Measured in PPM
Many water quality parameters depend on PPM values. These include chlorine, fluoride, nitrates, iron, hardness minerals like calcium and magnesium, and dissolved solids including salts. Some of these substances are helpful in the right amount, but harmful when too high.
For example, chlorine keeps water free from harmful microbes, yet chlorine above safe PPM levels causes irritation and health concerns. Fluoride helps protect teeth, but too much causes enamel damage.
Understanding PPM measurement helps maintain the ideal balance.
PPM Water Levels in Daily Life
Everyday water sources differ in PPM concentration due to their treatment and environment.
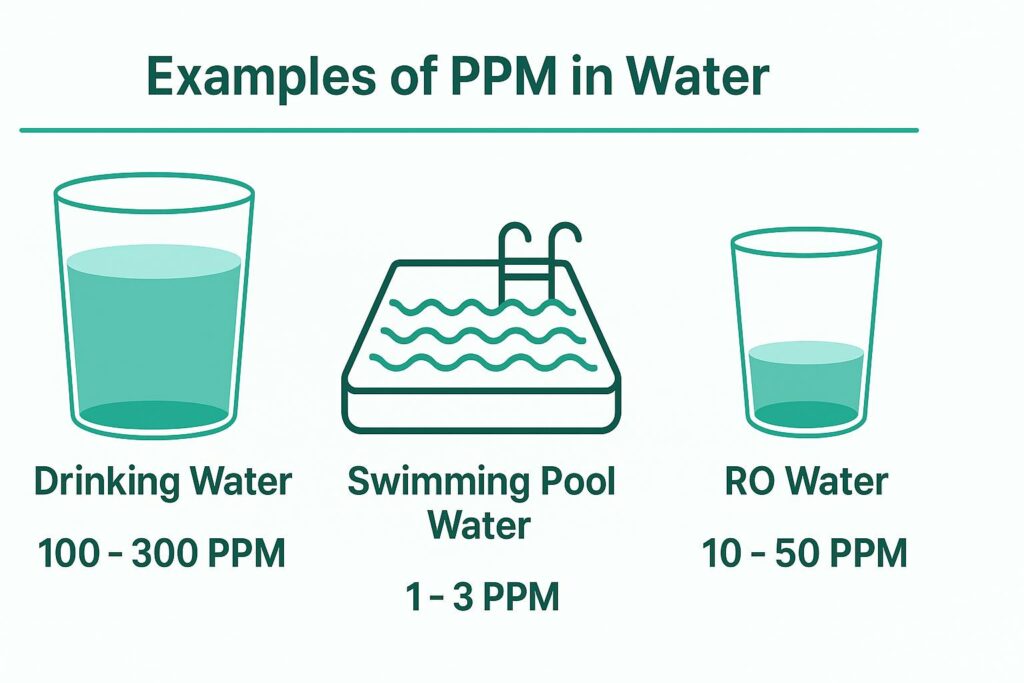
Example comparison
Tap water often contains 100 to 300 PPM of dissolved minerals.
Reverse osmosis water usually contains 10 to 50 PPM, making it cleaner.
Swimming pool water keeps chlorine around 1 to 3 PPM for hygiene.
Aquarium water must stay within safe PPM for fish health.
Each water type follows different water PPM standards based on its purpose.
How PPM Affects Water Taste
Higher PPM in water especially from minerals and salts, changes how water tastes. Water with very low PPM may taste flat, while water with very high PPM can taste bitter, salty or metallic. That is why bottled water companies carefully control PPM mineral content to maintain a desirable taste profile.
PPM in Drinking Water Quality
Drinking water should have a PPM range suitable for human consumption. Too high and it may contain harmful contaminants. Too low and it may lack natural minerals. Proper PPM water testing ensures safe hydration.
Example
If nitrate levels reach 50 PPM, the water may be risky for infants and must be treated.
If TDS (total dissolved solids) exceeds 500 PPM, taste and safety can decline.
So, knowing PPM concentration helps detect possible contamination early.
Measuring PPM in Water
PPM is easy to measure using simple home testing tools. TDS meters, chlorine test strips, aquarium test kits and pool testing kits all show PPM results instantly. Advanced laboratory instruments provide even more precise PPM readings for safety analysis and environmental testing.
Anyone can check water quality PPM at home and take action if values appear too high or too low.
Examples of PPM in Real Situations
If a home has water containing 300 PPM TDS, a filter may help improve taste and reduce scaling.
If aquarium water measures 0 PPM ammonia, fish stay healthy.
If pool water drops below 1 PPM chlorine, bacteria may multiply rapidly.
If borewell water reaches 700 PPM dissolved solids, a purification system becomes necessary.
These examples highlight why PPM water testing is a routine part of water management.
Why PPM Helps Protect Health
Many harmful contaminants are invisible. PPM concentration levels help identify substances that could cause stomach problems, long-term illness or toxicity. Monitoring even a slight increase in PPM of harmful chemicals protects families, pets, livestock and crops from potential waterborne risks.
Summary
PPM in water quality measures the amount of dissolved substances in one million parts of water. Although the numbers may seem small, these concentrations influence safety, taste, and hygiene. By understanding and monitoring PPM concentration, people can ensure their drinking water is clean, their aquariums remain healthy, and their pools stay sanitized. With regular water PPM testing, water quality remains easy to control and safe for everyday use.