PPM calculation is used to measure extremely small concentrations of substances in water, air, soil and solutions. The term PPM (parts per million) means one part of a substance is present in one million parts of the total mixture. Because many pollutants and chemicals exist in trace amounts, learning how to calculate PPM helps determine whether something is safe, clean or contaminated.
What Does PPM Mean
1 PPM represents one unit of substance in one million units of the mixture. Even though the concentration is tiny, it can still be meaningful. A few parts per million of chlorine, nitrates, carbon monoxide, or lead can affect health. That is why professionals use PPM measurements to make accurate decisions about safety.
Basic PPM Formula
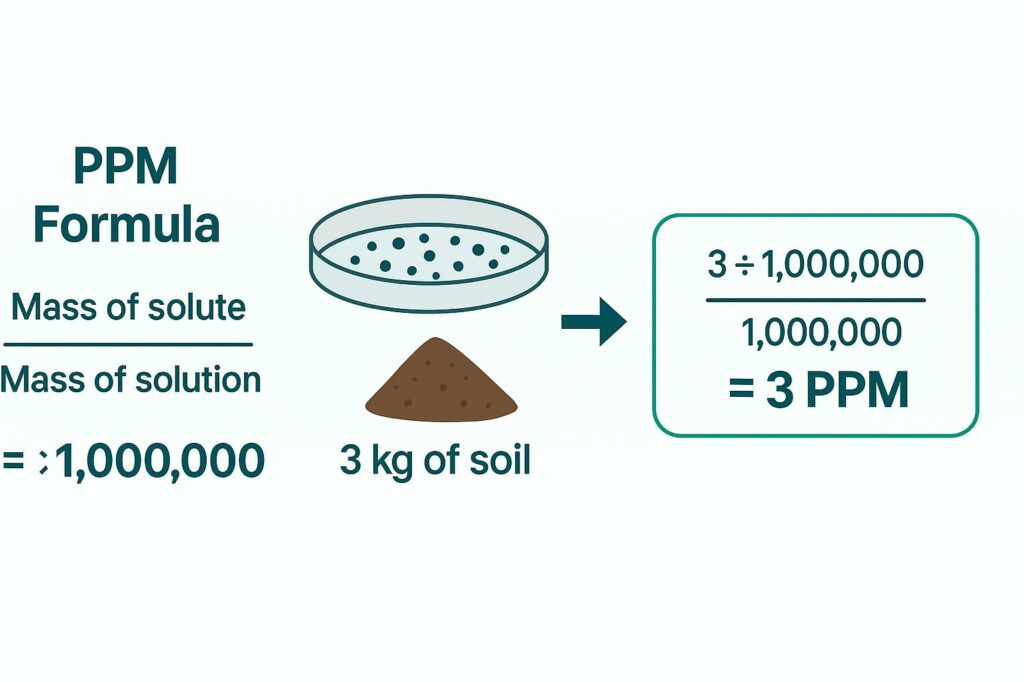
The most common formula used to calculate PPM is based on mass comparison.
PPM = (Mass of solute ÷ Mass of solution) × 1,000,000
This formula is helpful when both masses are known. It converts a tiny mass ratio into an easy-to-read number.
Example
A soil sample contains 3 mg of lead in 1 kg of soil.
PPM = (3 ÷ 1,000,000) × 1,000,000 = 3 PPM
So the soil contains 3 PPM of lead.
Table of PPM Examples in Water, Air, and Soil
| Sample Type | Example Measurement | Substance | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Quality | 2 PPM chlorine | Chlorine disinfectant | Water is properly sanitized for safe swimming |
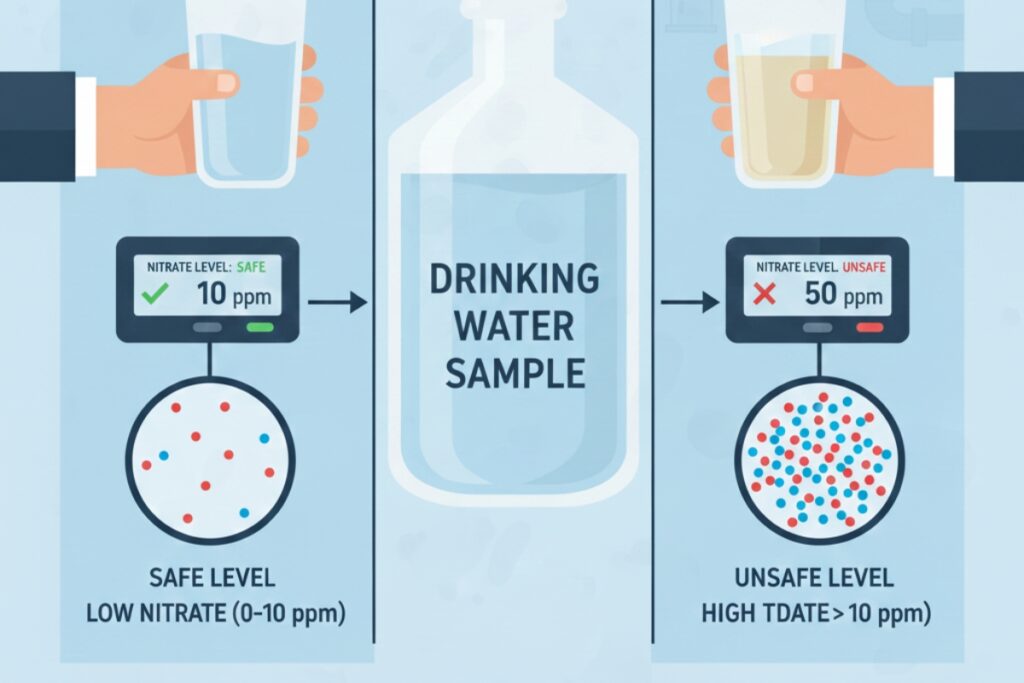
| Water Quality | 10 PPM nitrates | Nitrate contamination | Drinking water remains within recommended limits |
| Water Quality | 400 PPM TDS | Total dissolved solids | Water might taste salty or metallic |
| Air Quality | 1000 PPM CO₂ | Carbon dioxide indoors | Poor ventilation, reduced concentration and comfort |
| Air Quality | 0.07 PPM ozone | Ground-level ozone | May affect people with asthma and breathing issues |
| Air Quality | 5 PPM CO | Carbon monoxide | Dangerous concentration requiring immediate action |
| Soil Quality | 8 PPM iron | Plant micronutrient | Adequate level for crop nutrition |
| Soil Quality | 3 PPM lead | Heavy metal contaminant | Requires monitoring for food crop safety |
| Soil Quality | 20 PPM nitrates | Fertilizer nutrient | Supports healthy plant growth |
How to Calculate PPM in Water
Water quality often uses a simplified formula because 1 litre of water weighs one million milligrams. Therefore:
1 PPM = 1 mg per litre (mg/L)
This makes PPM calculation in water very straightforward.
Example
If a water sample contains 5 mg of chlorine per litre,
the concentration is 5 PPM chlorine.
This formula is used for drinking water, pools, aquariums, fish ponds, and wastewater testing.
How to Calculate PPM in Air
Gas concentrations depend on temperature and pressure, so PPM can require a more advanced formula. When mass concentration is known, scientists use the ideal gas relationship.
PPM = (Mass concentration × R × T) ÷ (MW × P × 1000)
R = universal gas constant
T = temperature in Kelvin
MW = molecular weight of gas
P = pressure in atmospheres
This ensures accurate PPM values for gases such as ozone, carbon monoxide, and VOC emissions.
Simplified Method for Gas PPM
Sometimes gas PPM is calculated using the mole fraction:
PPM = Mole fraction × 1,000,000
Example
If indoor air contains 0.001 CO₂ mole fraction,
PPM = 0.001 × 1,000,000 = 1000 PPM CO₂
This method is common in air sensors, ventilation control, and HVAC systems.
How to Calculate PPM Using Volumes
When mixing liquids by volume:
PPM = (Volume of solute ÷ Volume of solution) × 1,000,000
Example
If 2 mL of chemical is added to 200 litres of water,
PPM = (2 ÷ 200,000) × 1,000,000 = 10 PPM
This is used in industry, fuel additives, and food manufacturing.
How to Calculate PPM in Soil
Soil analysis uses a simple mg/kg formula:
PPM = mg of substance ÷ kg of soil
Example
If soil contains 10 mg nitrates per kg,
the soil concentration is 10 PPM nitrates.
Farmers use PPM soil testing to maintain proper nutrient levels for plant growth.
Converting PPM to Other Units

Because PPM fits between percentage and PPB, unit conversion is common.
PPM = % × 10,000
1 PPM = 1000 PPB
1 PPM = 0.0001%
Unit conversions help in scientific reports and regulatory standards.
Real-Life Examples of PPM Calculation
If aquarium water shows 0 PPM ammonia, fish are safe.
If pool water contains 2 PPM chlorine, disinfection is effective.
If indoor CO₂ rises above 1500 PPM, ventilation must be improved.
If drinking water has 400 PPM TDS, taste and safety may decline.
These examples show how PPM measurement influences daily decisions.
Why Learning PPM Calculation Is Important
How to calculate PPM is a useful skill in:
Water treatment
Air quality management
Environmental monitoring
Industrial standards
Food and agriculture
Laboratory safety
By monitoring PPM concentration, professionals can take action before contamination causes harm.
Summary
PPM calculation converts tiny amounts of substances into clear values that show how clean or polluted something is. Whether measuring chemicals in water, pollutants in air, or nutrients in soil, understanding how to calculate PPM helps protect health, improve quality, and ensure safety in scientific and everyday environments.
FAQ — How to Calculate PPM
What is the formula to calculate PPM
The most commonly used PPM formula is the ratio of the mass of solute divided by the mass of the solution, multiplied by 1,000,000. This converts a very small concentration into parts per million, which is easier to read and compare in scientific results.
How do you calculate PPM in water
To calculate PPM in water, simply measure the milligrams of substance per litre of water. Since one litre of water weighs one million milligrams, 1 mg/L equals 1 PPM. This formula is used in drinking water, pool water, aquariums, and wastewater testing.
How do you calculate PPM in air
PPM in air quality depends on gas volume and often requires temperature, pressure, and the ideal gas law. A simplified approach uses the mole fraction. Multiply the mole fraction of the gas by 1,000,000 to get PPM concentration in air.
What tools are used to measure PPM
A TDS meter measures water PPM, while gas sensors measure air PPM. Laboratory instruments calculate extremely low concentrations using advanced chemical analysis. These tools help ensure accurate PPM readings in environmental and industrial settings.
Can PPM be converted to other units
Yes. PPM conversions are common. One PPM equals 0.0001%. It is also 1000 times greater than PPB. Converting between these units allows scientists to report concentration values at different scales depending on the required precision.
Why is calculating PPM important
Knowing how to calculate PPM helps detect pollution, chemical safety issues, and contamination early. Many harmful substances are dangerous even at small PPM values, so accurate calculations protect health, environment, water quality, and industrial product safety.